Category
Campañas extranjeras
130 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
-
<p>The Protevs Swot 2018 campaign aimed to explore the South Balearic zone in early spring to observe the small scales of the oceanic mixed layer using high-resolution sampling devices.</p> <p>The area was chosen because it was positioned below the SWOT satellite's planned swath in its validation/calibration period. In this sense, it is a precursor experiment of experiments for the year 2022 and as such exploratory of the scales that will be observable by this newly designed altimetry satellite.</p> <p>A particular focus was placed on an anticyclonic structure in the southern Balearic Islands that is systematically detectable by altimetry but which appears to be an artifact.</p> <p>These samplings were combined with fine analysis of the surface content of small phytoplankton by flow cytometry to study the shaping of the marine landscape by frontal physical processes.</p> <p> </p>
-
<p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">The Protevs Swot 2018 campaign aimed to explore the South Balearic zone in early spring to observe the small scales of the oceanic mixed layer using high-resolution sampling devices.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">The area was chosen because it was positioned below the SWOT satellite's planned swath in its validation/calibration period. In this sense, it is a precursor experiment of experiments for the year 2022 and as such exploratory of the scales that will be observable by this newly designed altimetry satellite.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">A particular focus was placed on an anticyclonic structure in the southern Balearic Islands that is systematically detectable by altimetry but which appears to be an artifact.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">These samplings were combined with fine analysis of the surface content of small phytoplankton by flow cytometry to study the shaping of the marine landscape by frontal physical processes.</p>
-
Transit.
-
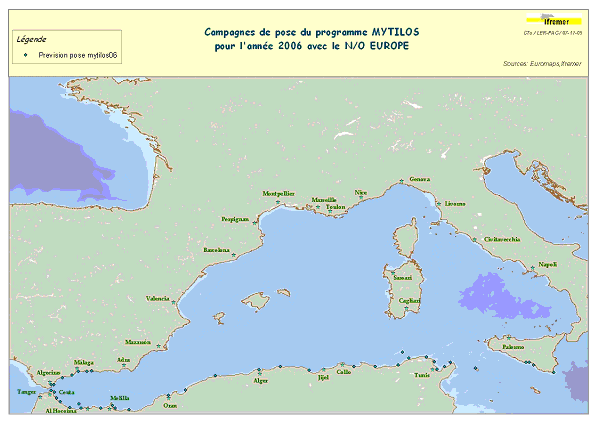
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. This falls under the 'MEDICIS' project.
-
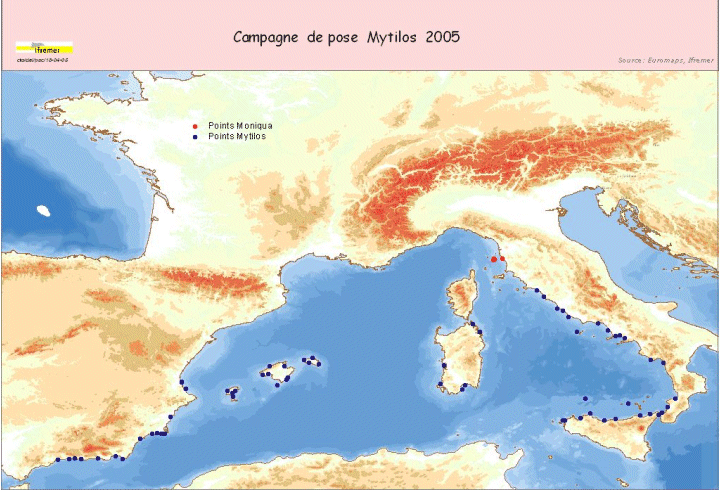
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 3 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel bed stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. 3) A study was run on the site of Livorno, taking bio-integrators, Posidonia and sediment samples to assess chemical contamination levels on 3 different matrices in the framework of the MONIQUA programme. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
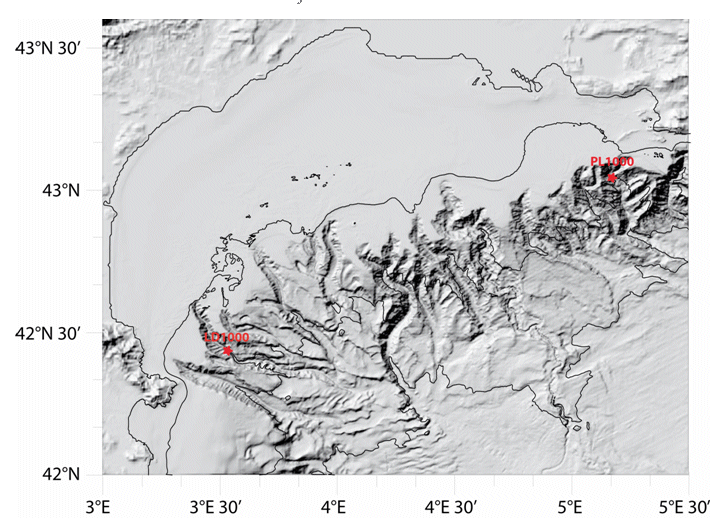
Characterizing the variability of hydrological and current measurement features and particulate fluxes in two canyons of Le Planier (station PL1000) and Lacaze-Duthiers (station LD1000) located at the easternmost and westernmost tips of the Gulf of Lion.
-
SHOM oceanographic cruise
-
<p style="text-align:justify">SHOM cruise with implementation of the MVP.</p>
-
Hydrography and physical oceanography cruise for the French Navy's hydrographic and oceanographic service (SHOM).
-
<p style="text-align:justify">The main objective of the observing system MOOSE is to monitor the long-term evolution of the north-western Mediterranean Sea (over more than 10 years) in the context of climate change and anthropogenic pressure in order to detect and identify the trend and environmental anomalies of the marine ecosystem. The MOOSE network aims to establish an integrated and multidisciplinary system in the Mediterranean Sea in accordance with the objectives of the national MISTRALS program (HyMeX, MeRMEX and ChARMeX). The MOOSE system is supported by national institutes (CNRS-INSU, French Ministry of Higher Education and Research) and involved different partners (Universities, IFREMER, Meteo France).</p> <p style="text-align:justify">The MOOSE network includes "multi-scale" measurement capabilities to accurately document the broad spectrum of hydrodynamic processes already identified (large scale eddies, mesoscale eddies, biogeochemical provinces). High temporal resolution measurements are obtained from fixed observatories (moorings, buoys) but their spatial distribution remains insufficient. Spatial variability is of the same order as temporal variability and understanding the evolution of this basin as a whole implies being able to dissociate both. Synergy with other strategies (ships, floats, gliders) is essential for the establishment of an observation network in such a system. To address the issues identified by MOOSE, two key areas of the north-western basin have been identified:</p> <ul> <li style="text-align:justify">The central and western part of the Ligurian Sea, which constitutes a homogeneous system isolated from direct coastal inputs by rivers and where atmospheric inputs are predominant (DYFAMED and ANTARES). It is also one of the entrance passages of the Intermediate Levantine Water (LIW) in the north-western Mediterranean basin.</li> <li style="text-align:justify">The central area of the Gulf of Lion where winter cooling leads to vertical mixing over 2000 m and sometimes to the bottom. The LION site (42°N 5°E) is ideal for studying the variability of winter convection to better understand mixing processes and dense water formation. It also characterizes the variability of the deep particle flow.</li> </ul> <p style="text-align:justify">Currently, fixed observation at these sites is carried out by six moorings:</p> <ul> <li style="text-align:justify">The Planier and Lacaze-Duthiers moorings composed of sediment traps and T/S sensors and current meters, for dense water cascading and particle export studies. These moorings have been set up since 1994 and managed by CEFREM.</li> <li style="text-align:justify">The LION mooring, consisting of a large number of T/S sensors, current meters, and two oxygen sensors, is in the Gulf of Lion convection zone. It has been deployed since 2007, and is managed by CEFREM and LOCEAN. A sediment trap near the bottom has also been present for 2 years in this area (LIONCEAU mooring). The latter will be integrated into the LION mooring in 2019.</li> <li style="text-align:justify">The ANTARES mooring is located in the North Current off Toulon and equipped with T/S sensors, current meters and oxygen sensors to quantify the bacteria activity and organic matter remineralization process in a deep marine environment. It exists since 2004, it is managed by the M.I.O. and the CPPM (Marseille). This mooring is part of the ERIC EMSO since 2017.</li> <li style="text-align:justify">The DYFAMED mooring, in the Ligurian Sea, equipped with sediment traps, T/S sensors, current meters and oxygen sensors to monitor the evolution of the water column, the impact of atmospheric dust deposition and marine particles export to deep waters. It exists since 1988, it is currently managed by the Oceanological Observatory of Villefranche-sur-Mer. This mooring is part of the ERIC EMSO since 2017.
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO