Format
XML
4301 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
-
The aims of this cruise were to elucidate the processes responsible for controlling iodocarbon concentrations and provide a dataset that can be used to develop modelled estimates of iodocarbon sea-air fluxes in tropical Atlantic waters.
-
Acoustic measurements.
-
<p>The Protevs Swot 2018 campaign aimed to explore the South Balearic zone in early spring to observe the small scales of the oceanic mixed layer using high-resolution sampling devices.</p> <p>The area was chosen because it was positioned below the SWOT satellite's planned swath in its validation/calibration period. In this sense, it is a precursor experiment of experiments for the year 2022 and as such exploratory of the scales that will be observable by this newly designed altimetry satellite.</p> <p>A particular focus was placed on an anticyclonic structure in the southern Balearic Islands that is systematically detectable by altimetry but which appears to be an artifact.</p> <p>These samplings were combined with fine analysis of the surface content of small phytoplankton by flow cytometry to study the shaping of the marine landscape by frontal physical processes.</p> <p> </p>
-
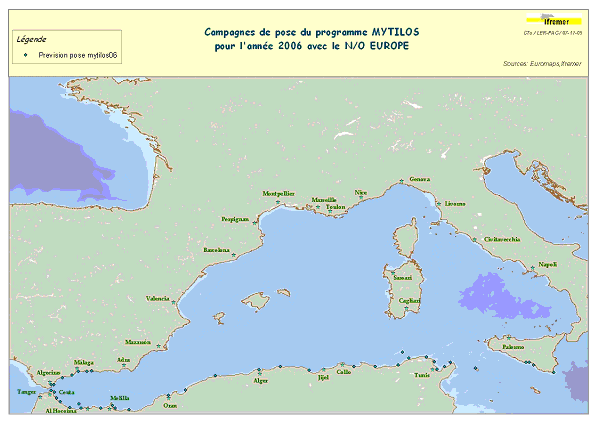
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. This falls under the 'MEDICIS' project.
-
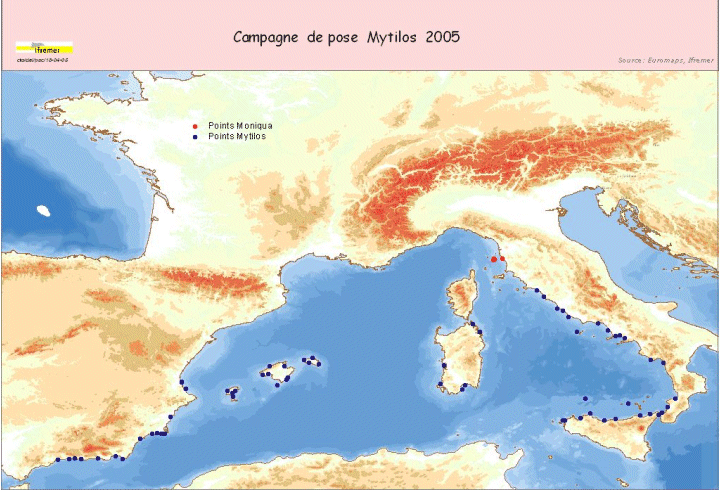
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 3 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel bed stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. 3) A study was run on the site of Livorno, taking bio-integrators, Posidonia and sediment samples to assess chemical contamination levels on 3 different matrices in the framework of the MONIQUA programme. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
<p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">The Protevs Swot 2018 campaign aimed to explore the South Balearic zone in early spring to observe the small scales of the oceanic mixed layer using high-resolution sampling devices.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">The area was chosen because it was positioned below the SWOT satellite's planned swath in its validation/calibration period. In this sense, it is a precursor experiment of experiments for the year 2022 and as such exploratory of the scales that will be observable by this newly designed altimetry satellite.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">A particular focus was placed on an anticyclonic structure in the southern Balearic Islands that is systematically detectable by altimetry but which appears to be an artifact.</p> <p style="margin-left:0cm; margin-right:0cm">These samplings were combined with fine analysis of the surface content of small phytoplankton by flow cytometry to study the shaping of the marine landscape by frontal physical processes.</p>
-
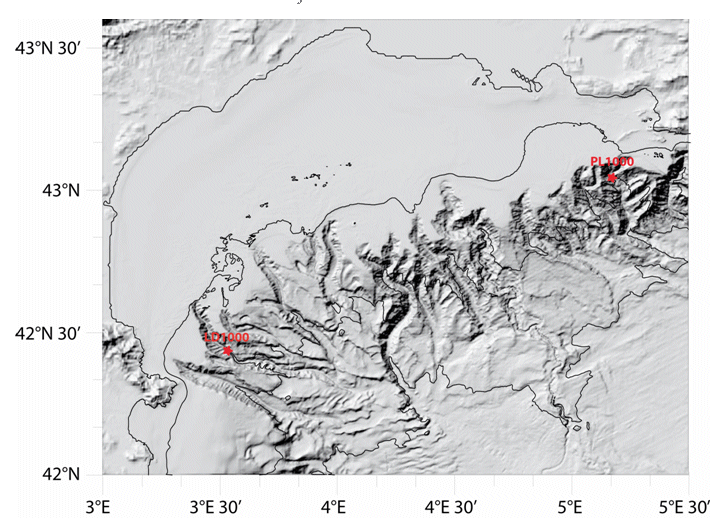
Characterizing the variability of hydrological and current measurement features and particulate fluxes in two canyons of Le Planier (station PL1000) and Lacaze-Duthiers (station LD1000) located at the easternmost and westernmost tips of the Gulf of Lion.
-
The cruise is a component of RAPID-WATCH, whose objectives are: to deliver a decade-long time series of calibrated and quality-controlled measurements of the Atlantic MOC from the RAPID-WATCH array and; to exploit the data from the RAPID-WATCH array and elsewhere to determine and interpret recent changes in the Atlantic MOC, assess the risk of rapid climate change, and investigate the potential for predictions of the MOC and its impacts on climate. Objectives of this cruise: to recover, calibrate and redeploy moorings from the eastern boundary and mid-Atlantic ridge subarrays of the 26.5N line of RAPID moorings.
-
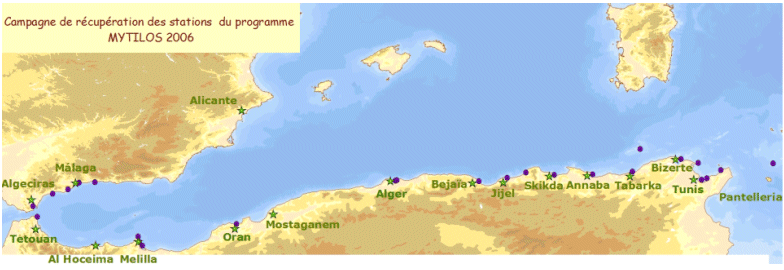
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 2 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Sicily (Italy), including Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. 2) Sediment samples in addition to mussels samples were taken upon the partners' request. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
<p>The purpose of WestMedFlux is to study thermal fields in ocean-continent transition zones in the Western Mediterranean, and the role of fluids and salt diapirs on the thermal field.</p>
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO