Creation year
2007
191 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
Scale
-

Datos de temperatura y salinidad superficial registrados por el termosalinógrafo del B/O Naváz en la zona de la Ría de Baixas y plataforma continental adyacente.
-
The aims of this cruise were to elucidate the processes responsible for controlling iodocarbon concentrations and provide a dataset that can be used to develop modelled estimates of iodocarbon sea-air fluxes in tropical Atlantic waters.
-
Overall objectives in the EU GO project are to assess the promising potential of seismic imaging for physical oceanography, in view of its combination of fine resolution and coverage unmatched by conventional oceanographic measurements. D318 was to provide the means of assessment by obtaining a unique, comprehensive, oceanographic and seismic dataset at the same time and place. Specific objectives for R.R.S. Discovery cruise 318a were to deploy four ADCP moorings, three adjacent temperature-logger moorings and STABLE, in an L-shape array in 750-1000m depth east of Portimao Canyon, carrying out adjacent CTD stations, deploy two OBH moorings, carry out seismic sections using the Ifremer high-frequency air-guns and streamer, accompanied by regular XBT and less frequent XCTD casts. In addition underway data was logged including ship-borne ADCP, surface temperature and salinity, meteorology, gravity and magnetics (to test new NERC magnetometers).
-
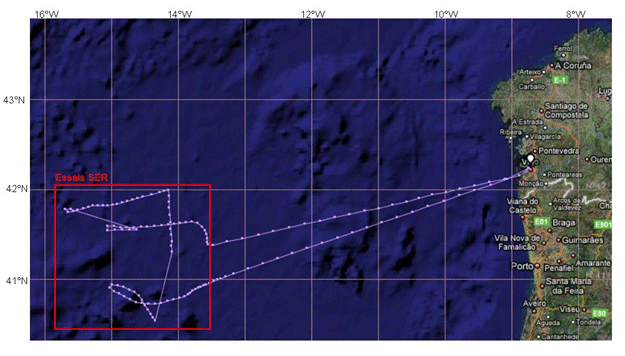
Technological trials run on seismic equipment developed by the SERCEL firm.
-
SHOM cruise between Lisbon and Toulon
-
This cruise was completed as part of the United Kingdom Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) funded RAPID Programme to monitor the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at 26.5ºN. The primary purpose was to service the Eastern Boundary and Mid-Atlantic ridge sections of the 26.5ºN mooring array. The Rapid-MOC array of moorings was deployed across the Atlantic to set up a pre-operational prototype system to continuously observe the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC). This array will be further refined and refurbished during subsequent years as part of the Rapid-WATCH programme. The instrumentation deployed on the array consists of a variety of CTD loggers, current meters, bottom pressure recorders, and Inverted Echo-sounders, which, combined with time series measurements of the Florida Current and wind stress estimates, can be used to determine the strength and structure of the MOC.
-
SHOM cruise between Brest and Lisbon
-
The objectives of the BELMER project are: - to validate the MERIS water products for Belgian coastal waters and neighbouring French, UK and Dutch waters - to provide a quantitative statement of product accuracy and recommendations for improvements in the scientific algorithms, where appropriate. In particular the problems reported by the MERIS validation and user communities of turbid water atmospheric correction, case 2 water chlorophyll retrieval, adjacency effects (straylight), moderate sunglint, spatio-temporal variability of specific inherent optical properties and bottom reflectance will be addressed. This project is funded by the "PROgramme for the Development of scientific Experiments" (PRODEX) of the European Space Agency (ESA).
-
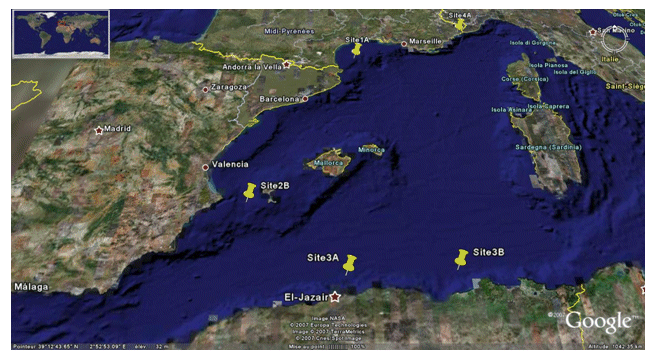
<p>The PRISME cruise objectives were to: - quantify the risk of earthquake-induced sedimentary liquefaction (for areas studied on the Algerian margin and slope off Nice, France); - quantify the risk of instability and failure due to loss of resistance in sensitive clay (slope off Nice); - quantify the risk of slope breaks and erosion caused by bottom currents (canyon heads - gulf of Lion); - identify the triggering factors for slides seen off Ibiza; - and begin to identify the turbidity related to seismic activity along the Algerian margin. This falls under the ANR-Isis an dGDR Marges projects. The cruise took place on 5 sites: Site 1A - Gulf of Lion - North: N 42° 50.00' South: N 42° 40.00' West: E 003° 35.00' East: E 004° 0.00' / Site 2B - Ibiza channel - North: N 38° 39.00' South: N 38° 37.50' West: E 000° 47.00' East: E 000° 51.00' / Site 3A - Alger - North: N 37° 30.00' South: N 36° 40.00' West: E 002° 00.00' East: E 004° 00.00' / Site 3B - Djijel North: N 37° 30.00' South: N 37° 00.00' West: E 005° 00.00' East: E 004° 00.00' / Site 4A - Djijel North: N 43° 40.00' South: N 43° 38.00' West: E 007° 12.00' East: E 007° 15.00'.</p>
-
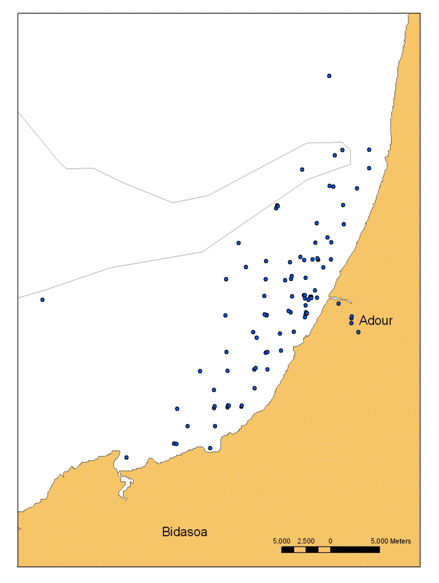
The BATEL-1 cruise was conducted from 4 to 14 June 2007 by the University of Bordeaux-1 (EPOC laboratory). The main objective was to obtain a database of optical and geochemical data in order to create algorithms to quantify the suspended particles and dissolved substances for the interpretation of MODIS, SPOT, ASTER and FORMOSAT-2 satellite images. The end purpose is to identify coastal water composition from satellite images. The second aim was to monitor the Adour river's turbidity plume during this period. In addition, measurements were taken to analyze the heavy metals, stratification of water masses (CTD) and for intercomparison of two fluorimeters. These measurements are currently being used by Ms. Petus (Thesis, Cifre grant). The cruise fell under the interregional Aquitaine-Euskadi programme.
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO