Creation year
2005
91 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
-
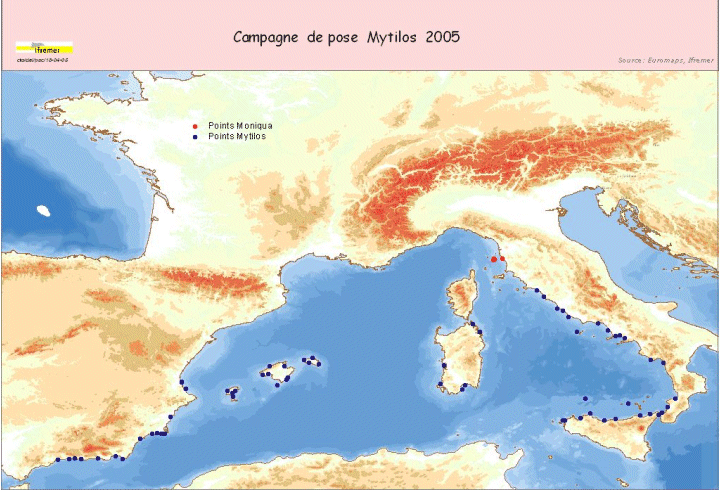
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 3 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel bed stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. 3) A study was run on the site of Livorno, taking bio-integrators, Posidonia and sediment samples to assess chemical contamination levels on 3 different matrices in the framework of the MONIQUA programme. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
CD170 was a collaborative cruise with the Knorr cruise KN182_2. The latter cruise was conducted between 2 May 2005 and 26 May 2005. These cruises were completed as part of the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) funded RAPID Programme and the US National Science Federation (NSF) funded MOCHA Programme to monitor the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at 26.5 degrees North. The primary purpose of both cruises was to service the 26.5 degrees North mooring array deployed in 2004 during RRS Discovery cruises D277 and D278. These cruises are the first annual refurbishment of this array.
-
Beautemps-Beaupré cruise.
-
Investigations at the dumpsite for low-level radioactive waste at the Iberian Deep Sea Plain
-
Beautemps-Beaupré cruise.
-
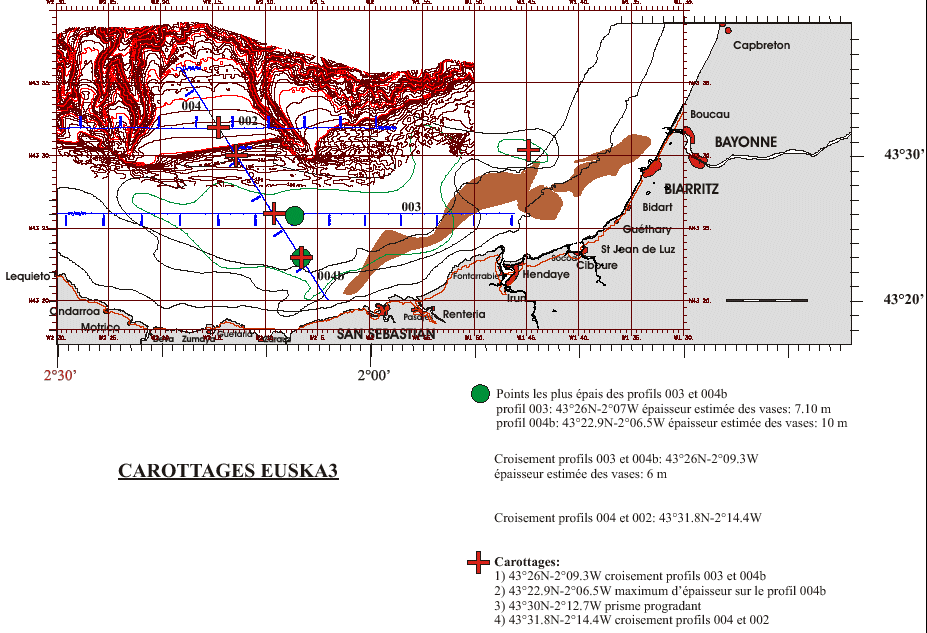
Core sampling on the mudflat of the Basque continental shelf. This falls under the Aquitaine / Euskadi project.
-
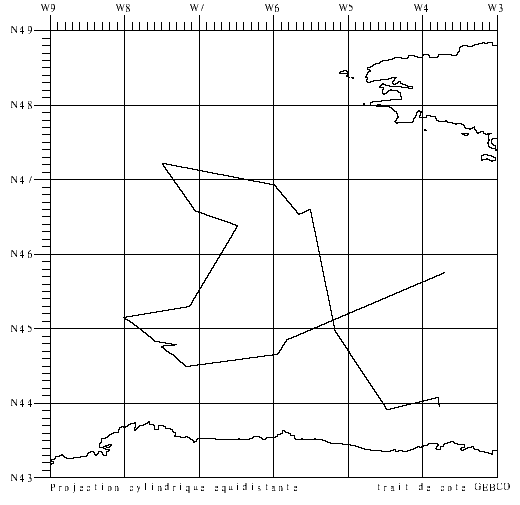
-Validation of surface salinity measurements using drifting buoys. Three models of drifting buoys (17 buoys in all) were deployed in the Bay of Biscay on 2 April (R/V Thalassa trip) and on 2-3 May (COSMOS1 aboard Côtes de la Manche). This involved passing close to the buoys, taking samples, TSG measurements and CTD hauls to validate the data. Two sections taken by CTD probe in front structure eddy (for the CONGAS programme). Retrieval of a prototype PROVOR-CTS3 float deployed in May by the Côte d'Aquitaine vessel. 9 CTD sensors to be attached to elephant seals were tested (mounted on SBE25 CTD during profiles). This falls under the COSMOS project, headed by J. Boutin and G. Reverdin.
-
Beautemps-Beaupré cruise.
-
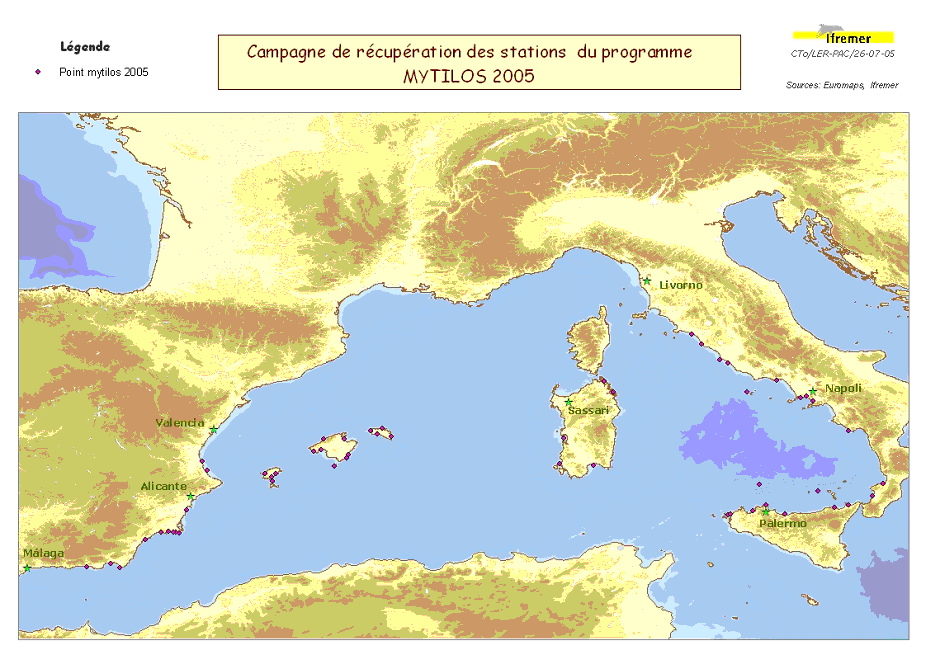
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 2 major actions: 1) Retrieving artificial mussel bed stations immersed in March with R/V l'Europe along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. This falls under the MYTILOS project.
-
The goal of this cruise was to recover and redeploy some RAPID-MOC moorings near the Eastern Boundary as part of our six-month turnaround programme. Specific cruise objectives were to: 1. Recover moorings EB1 (24 microcats) and EB2 (MMP profiling from 50m to 2500m with microcats and current meters below), two principal tall eastern boundary moorings, sited on a Topex crossover point near 24N, 24W. 2. Redeploy EB1 (24 inductive microcats plus the telemetry system) and EB2 (MMP mooring). 3. Deploy EBADCP to replace the instrument deployed in April but trawled after 10days and recovered by the R/V Poseidon. 4. Deploy two URI Pressure Inverted Echo Sounders. One deployed in 1000m and one in 5000m next to the BPR lander at mooring EB1. 5. CTD stations for pre and post deployment calibrations of all mooring instrumentation. 6. Search for and if possible recover MMP mooring EB2 deployed in April 2004 and located 100km north south of Gomorra in October 2004.
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO