Keyword
L'Europe
20 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
-
The series of PELMED cruises began in 1993. Their objective is to assess small pelagic resources in the Gulf of Lion, using the echo-integration method and trawling to identify the detections observed. Until 2007, each cruise consisted in systematically prospecting from Port-Vendres to Marseille, along 9 legs set 12 nautical miles apart, perpendicular to the coast, in daytime (6 am to 9 pm), along the entire width of the continental shelf. Acquisition along legs for acoustic prospection covered 440 nautical miles and the catches from trawling to identify the structures encountered led to a complete analysis: number and weight by species, size sampling, otolith samples taken in order to construct size-age keys for sardines, anchovies and hake, updating of biological parameters.
-
Characterizing the variability of hydrological and currentometric features and particulate fluxes on the continental rise of the Gulf of Lion et and in the deep convection zone. Monitoring of deep benthic communities in western canyons and on the continental rise of the Gulf of Lion. This fell under the HERMIONE project.
-
Characterizing the variability of hydrology and currentology features and particulate fluxes in the two canyons of Planier (station PL1000) and Lacaze-Duthiers (station LD1000), located at the eastern and western edges of the Gulf of Lion.
-
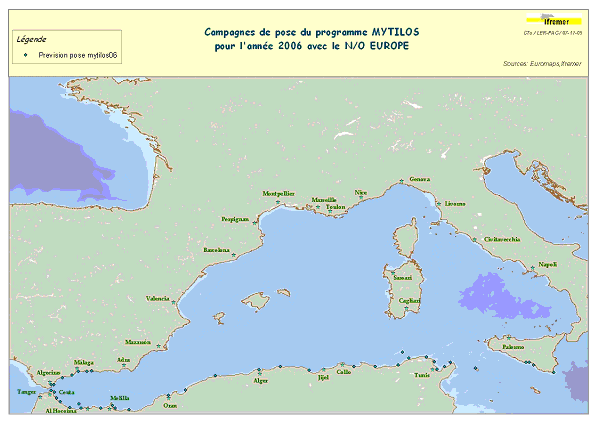
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. This falls under the 'MEDICIS' project.
-
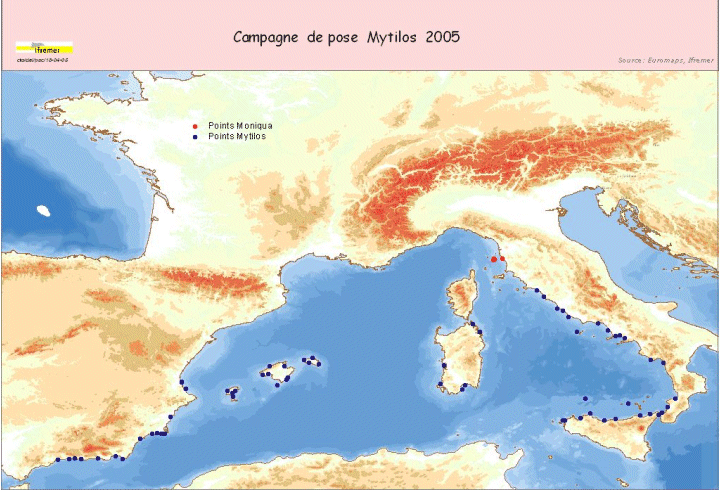
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 3 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel bed stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. 3) A study was run on the site of Livorno, taking bio-integrators, Posidonia and sediment samples to assess chemical contamination levels on 3 different matrices in the framework of the MONIQUA programme. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
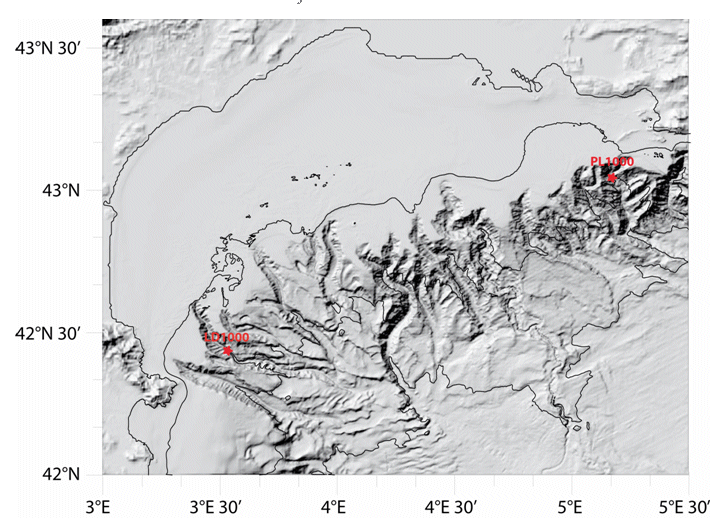
Characterizing the variability of hydrological and current measurement features and particulate fluxes in two canyons of Le Planier (station PL1000) and Lacaze-Duthiers (station LD1000) located at the easternmost and westernmost tips of the Gulf of Lion.
-
Small pelagic fish are both the keystone species of the ecosystem because of the central position they hold in the food chain and represent highly significant economic stakes for fisheries since they make up the majority of landings in the French Mediterranean (approximately 50% of catches for sardines and anchovies; Demaneche et al. 2009). So, to assess stocks and propose appropriate management methods, it is important to have both good knowledge about these species and independent fisheries data. Ifremer's fisheries science laboratory in Sète has monitored these populations since the 1990s. In 2002, the EU asked Member States to formalize certain operations by contract, in this context, the PELMED cruise was part of the extended contractual programme for biomass assessment (DCF). Therefore, each year France is obliged to assess the biomass of small pelagic species in the Mediterranean, in order to determine the stocks' status and propose management measures. These assessments are carried out in the framework of the general fisheries commission for the Mediterranean (CGPM). Since numerous countries had begun monitoring these species using acoustic methods, the MEDIAS (MEDIterannean Acoustic Surveys) scientific group was created in 2008 with the objective of standardizing the protocols. Finally, national management plans for Gulf of Lion fisheries were set up in 2014 (particularly for pelagic trawlers and purse seines) with scientific objectives touching on the biomass of small pelagics. The PELMED cruise, whose main aim is to directly assess the small pelagics biomass, is conducted therefore in a clearly institutional framework (national, European and Mediterranean). However, the scientific stakes remain just as important. Since 2008, a special situation has been observed in the Gulf of Lion, where the biomasses of sardines and anchovies (and even mackerel) have decreased synchronously. Even more unexpectedly, although the recruitment rates observed over the past few years in the species are particularly high, the populations don't seem to be growing back and their biomass is continuing to drop. This is particularly surprising in a marine ecosystem where recruitment is generally considered to be the determining factor of population dynamics for species with a short life span. The collection of biological parameters on species of small pelagics done during the previous PELMED cruises made it possible to highlight significant demographic changes (loss of large age classes, decrease in size, poorer body condition) which seem to suggest "bottom-up" population control. Therefore, the ecosystem-based nature of the PELMED cruises (from physical parameters to top predators, not to mention phyto- and zooplankton and fodder fish) appears to be crucial in understanding the dynamics of these populations. It was decided this year to stop prospecting the Catalan Sea, in order to extend the spatial coverage to the east of the Gulf in the PACA region (from Marseille to Nice). Since the narrowness of the shelf in this zone does not allow for prospecting along "classic" legs, the objective will be to validate a prospection method which is adapted to the area.
-
Assessment of small pelagic species resources in the Gulf of Lion using echointegration and trawl hauls to identify the observed echoes. This fell under the SIDEPECHE project.
-
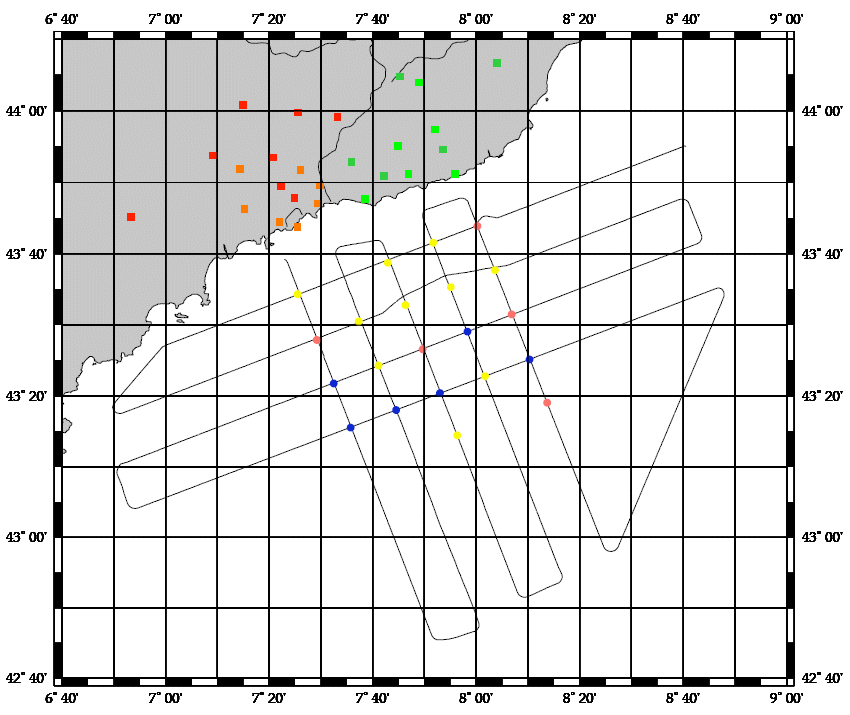
Assessment of small pelagic species resources in the Gulf of Lion using echo-integration and trawl hauls to identify the observed echoes. This falls under the SIDEPECHE project.
-
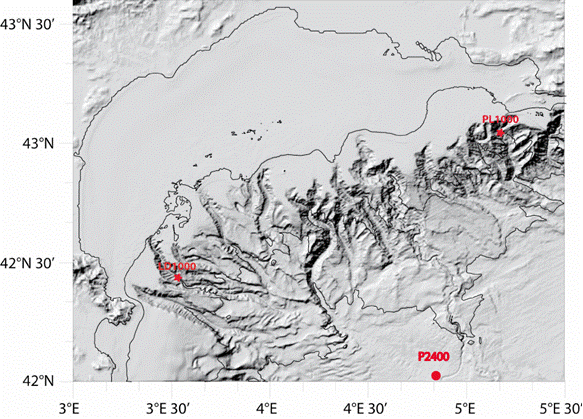
Characterizing the variability of hydrological and current measurement features and particulate fluxes in two canyons of Le Planier (station PL1000) and Lacaze-Duthiers (station LD1000) located at the easternmost and westernmost tips of the Gulf of Lion. Since 2011, setting up a long-term frame of reference in the convection zone - PPS3 trap, buoy zone and LION line.
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO