Keyword
143
9 record(s)
Type of resources
Categories
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Status
-
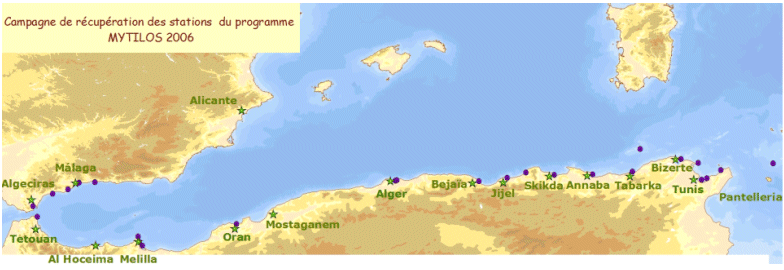
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 2 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Sicily (Italy), including Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. 2) Sediment samples in addition to mussels samples were taken upon the partners' request. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
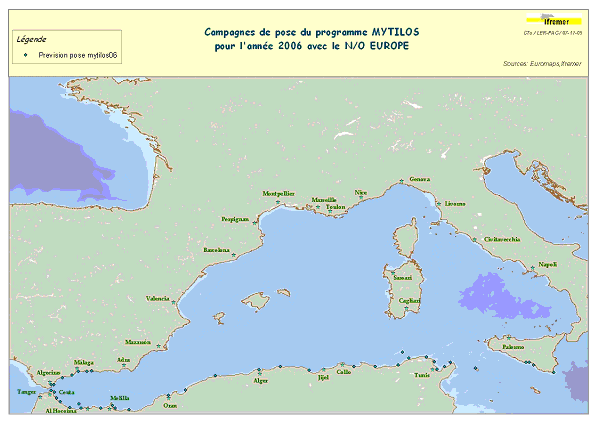
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, Morocco, Tunisia, Sicily canal), using artificial stations of mussels. The MYTILOS1 cruise aimed to utilize the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean, in the northern part of the NW Basin. Experiments run in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER were to be extended to Southern Mediterranean coasts, i.e. Spanish, Moroccan, Algerian and Tunisian coasts, as well as the Sicily Canal in Italy, on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data from MYTILOS2 cruise will supplement those obtained in 2004 and 2005 during the RINBIOC1 and MYTILOS1 cruises by including the coasts of North Africa, Southern Spain and the island of Pantelleria. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget drawn up in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. This falls under the 'MEDICIS' project.
-
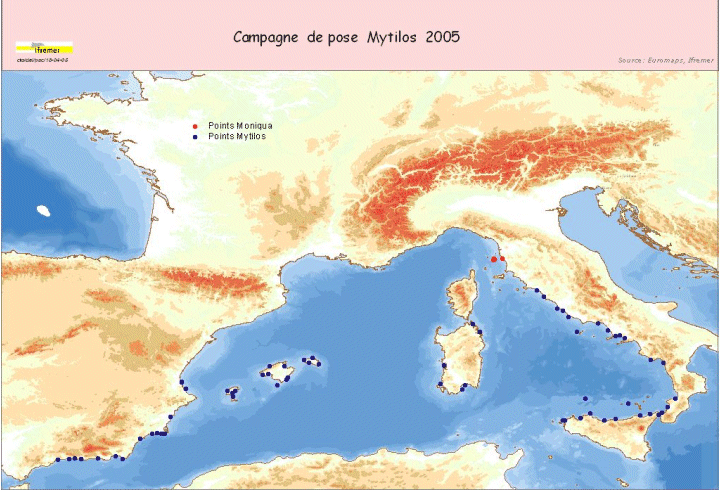
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 3 major actions: 1) Artificial mussel bed stations were placed and recovered along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. 3) A study was run on the site of Livorno, taking bio-integrators, Posidonia and sediment samples to assess chemical contamination levels on 3 different matrices in the framework of the MONIQUA programme. This falls under the MEDICIS project.
-
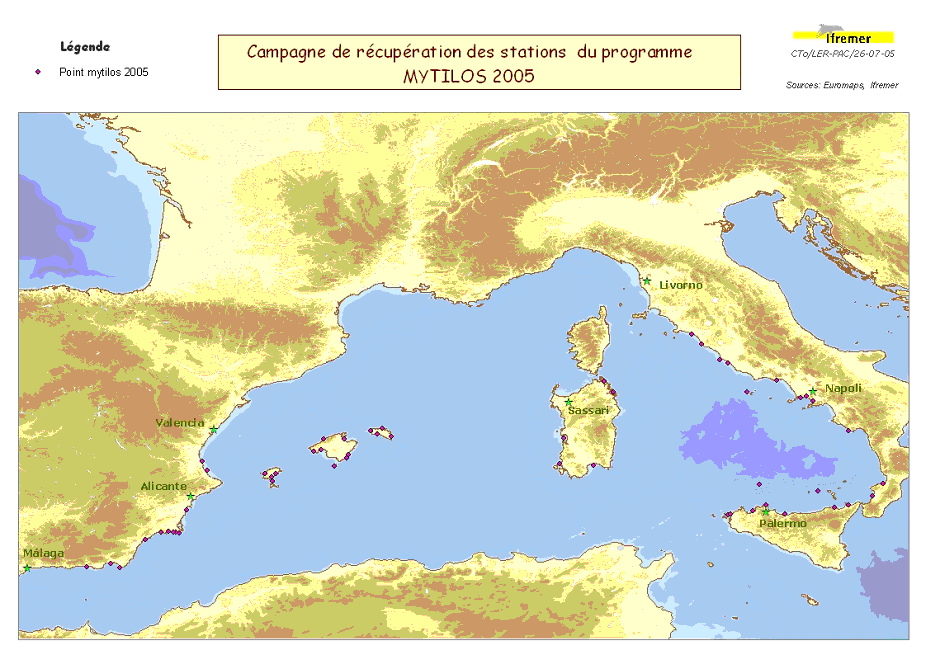
Assessment of chemical contamination in coastal water masses (Spain, France, Italy), using artificial stations of mussels and passive sensors. The MYTILOS 1 cruise aimed to use the RINBIO network methodology around the western Mediterranean. Experiments done in the French Mediterranean since 1996 by IFREMER will be extended to Spanish and Italian Mediterranean coasts on the basis of a standardized protocol. The data will supplement those obtained in 2004 during the RINBIOC1 cruise by including the islands of the western basin, the south of Spain and Italy. In addition, the results will be used to complement the chemical contamination budget made in the framework of the European Water Framework Directive's implementation. The survey was based on 2 major actions: 1) Retrieving artificial mussel bed stations immersed in March with R/V l'Europe along a shoreline between Malaga (Spain) and Rome (Italy), including the Balearic Islands, Sardinia and Sicily. 2) Gellyfish-type "passive" sensor stations were deployed along with some of the artificial mussel bed stations. This falls under the MYTILOS project.
-

Cr Contra75 ref. B2945799.975 ICES created form
-

In this Cruise Plan we present a strategically collected suite of sediment coring stations that may help to study fluid flow system in the northern Tunisian margin extending to the Tyrrhenian Sea.
-

ISLAND is a research cruise that will address the above issues through the following 3 specific objectives: a) To explore how the NW Sicilian canyons evolved during the Late Quaternary (differences in style, frequencies and intensity of sedimentary flows, possible differences in forcing mechanisms) and to assess which canyon(s) is/are more “active” in the present-day conditions and why. b) To establish whether canyons displaying different morphologies and controlled by different processes may be characterized by differences in the spatial distribution and variability of benthic biomass and biodiversity (are the most active canyons always the most biodiverse?). c) To explore the role of bottom trawling fishery in shaping the morphology and governing the presentday dynamics of submarine canyons and eventually assess its impact in altering canyon biodiversity (is trawling activity affecting the natural canyon seascapes and sedimentary dynamics, inducing a change in biodiversity?).
-

TAlPro-2016 represents the Western Mediterranean basin component of the MedSHIP initiative. The cruise will occupy two meridional sections, one across the relatively flat and deep Algero-Provencal basin, and one across the deep and rugged Tyrrhenian Sea. The data collected during these sections will allow to: 1) measure the changes in the thermohaline properties of Mediterranean water masses at the basin-scale; 2) quantify the Dissolved Inorganic Carbon (DIC) storage in the Western Mediterranean Sea; 3) quantify the uptake of anthropogenic carbon in the Western Mediterranean Sea; 4) quantify changes in the ventilation of the deep and intermediate water masses thanks to the transient tracers (CFCs and SF6).
-

The main objectives for the MedSeA cruise are to: - Refine climatological maps of carbonate species distribution (pH, pCO2, CO32-, CT, AT, CaCO3 saturation states), along with their isotopic signatures, in the Mediterranean Sea. - Report on the determination of the anthropogenic carbon distribution throughout the whole Mediterranean Sea and its associated uncertainty estimate - Determine the effects of carbonate chemistry on Mediterranean calcifying and non-calcifying planktonic organisms. - Determine synergistic effects of acidification, warming and nutrients on key pelagic organisms. - Identify and quantify responses of fundamental Mediterranean biogeochemical processes to acidification and warming. - MedSeA is carried out in collaboration with the Geotraces program in order to collect water for chemical large volume trace elements and isotopes such as Th/Pa, Artificial radionuclides, Th-234, Nd-isotopes and Ra.
 Catálogo de datos del IEO
Catálogo de datos del IEO